Basic Cellular System
In this blog, we are going to cover and explore the basic cellular system. The following concepts we going to learn in this blog -
- What are the basic units of a cellular system?
- What are various mechanisms for capacity increase in cellular systems?
- Why hexagonal cells are used in cellular systems?
- What are the performance criteria of mobile communication?
(i) What are the basic units of a cellular system?
A cell site, a mobile unit, and a mobile telephone switching office (MTSO) are the main parts of the basic cellular system. A basic cellular system connection to link the three subsystems is shown in the figure.
(1) Mobile Units - A mobile telephone unit has a control unit, a transceiver, and an antenna system.
(2) Cell Site - The interface between the MTSO and the mobile units is given by the cell site. The cell site contains a control unit, radio cabinets, antennas, a power plant, and data terminals.
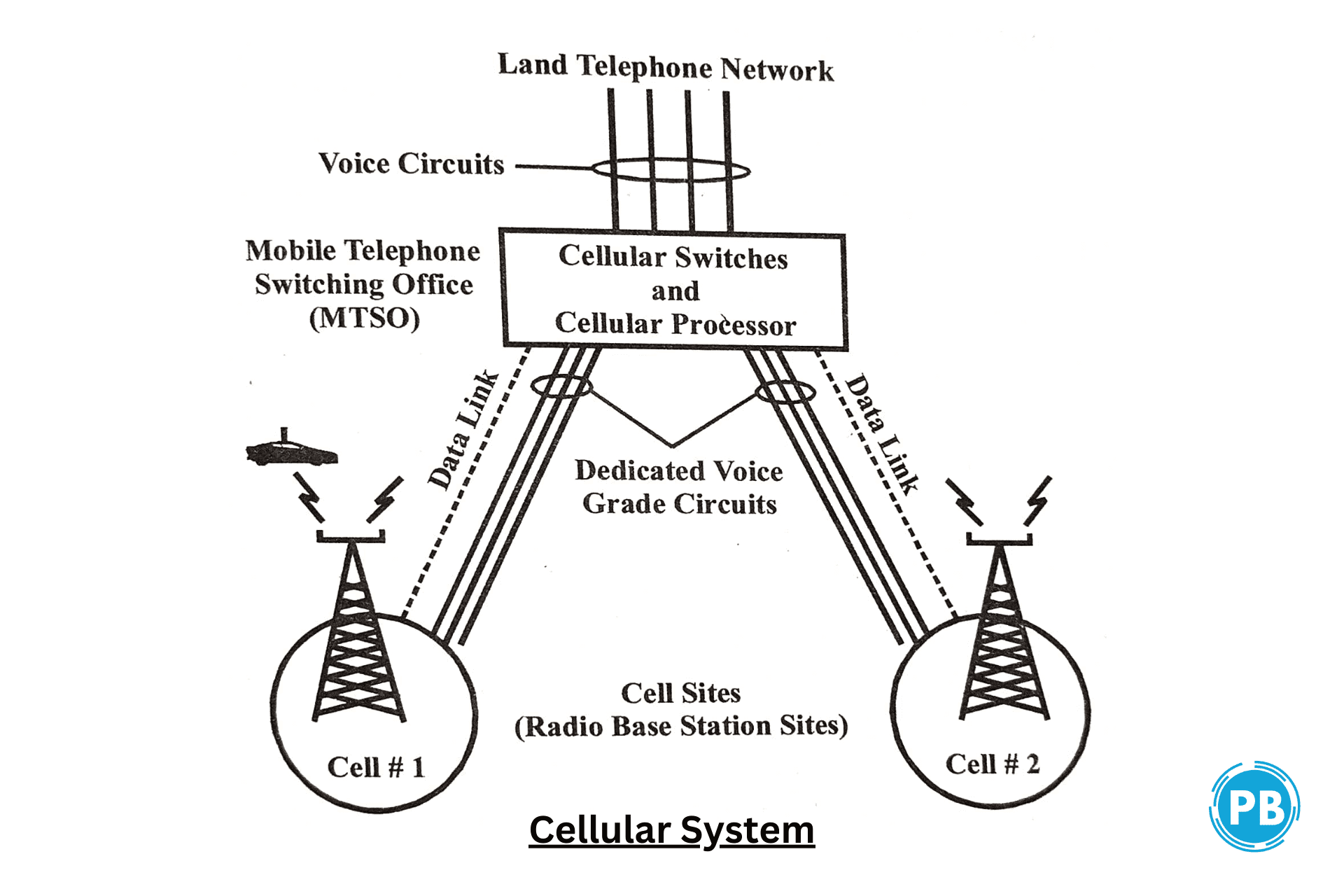
(3) Connections - The three subsystems are connected by the radio and high-speed data links. Only one channel can be used by each mobile unit at a time for its communication link. But, the channel is not fixed. It may be anyone in the whole band allocated by the serving area with each site having multichannel capabilities which can connect simultaneously to several mobile units.
(4) MTSO - The mobile telephone switching office is the central coordinating element for all cell sites, which has the cellular processor and cellular switch. MTSO interfaces with telephone company zone offices handles call processing, and manages billing activities.
MTSO provides the capability to handoff calls in progress, as the mobile terminal user moves between cells in the cellular system. If possible the handoff should be transparent to the user in terms of interruption and (or) call failure.
Handoff between channels may also be required for other reasons (e.g. load balancing, emergency call handling, meeting requirements, or transmission quality)
(ii) What are various mechanisms for capacity increase in cellular systems?
The following approaches are used in cellular systems to increase the capacity -
(i) Small Cell Size - If we can control the radiation pattern we can reduce the size of the cell and increase the traffic capacity. This approach is based on the assumption that all the mobile units are identical, including the mobile antennas and their mountings.
(ii) Queuing-Queuing of handoff calls can increase traffic capacity.
(iii) Enhanced Frequency Spectrum-Cellular mobile industries have been allocated an additional 166 voice channels. With an enhanced frequency spectrum, traffic capacity is increased.
(iv) Dynamic Channel Assignment - Dynamic, rather than fixed, channel assignment is another means of increasing traffic capacity.
(iii) Why hexagonal cells are used in cellular systems?
Cellular Concept and Hexagonal Cells - The hexagonal shape was chosen because it provides the most effective transmission by approximating a circular pattern while eliminating gaps inherently present between adjacent circles.
The fundamental concepts of cellular telephones are quite simple. The FCC originally defined geographic cellular radio coverage areas. With the cellular concept, each area is further divided into hexagonal-shaped cells that fit together to form a honeycomb pattern.
(iv) What are the performance criteria of mobile communication?
The performance criteria of mobile systems are categorized into three types as follows -
(i) Voice Quality - Voice quality is very difficult to test without subjective tests from the customer's views. In this technical section, engineers cannot decide how to make a system without knowing the voice quality that will satisfy the subscriber's needs.
The situation is different in military communications -armed forces personnel should employ the allocated equipment.
The voice quality, in the case of any given commercial communications system, will be dependent upon the following criterion -
a set value x at which y% of users rate the system voice quality (from transmitter to receiver) as good or excellent, the last two circuit merits (CM) of the five given as under-
| CM | Score | Quality Scale |
| CM1 | 1 | Unsatisfactory (speech is not understandable) |
| CM2 | 2 | Poor (speech understandable only with considerable effort, frequent repetitions required) |
| CM3 | 3 | Fair (speech understandable with a slight effort, occasional repetitions required) |
| CM4 | 4 | Good (speech easily understandable, some noise) |
| CM5 | 5 | Excellent (speech accurately understandable) |
The cost of making the system increases as the percentage of users selecting CM4 and CM5 rises.
The mean opinion score (MOS) is the average of the CM scores achieved by all the listeners. Generally, the toll-quality voice is around MOS ≥ 4.
(ii) Service Quality - Three terms are needed for service quality -
(a) Coverage - The system should provide services to an area as high as possible. However, with radio coverage due to irregular terrain configurations, it is generally impractical to cover 100% of the area for two reasons -
(1) Transmitted power would have to be very large to illuminate weak spots with appropriate reception, a significant added cost factor.
(2) When transmitted power is very high, it becomes harder to control interference.
Thus, systems usually attempt to cover 75% of an area in hilly terrain and 90% of an area in flat terrain. Combined voice quality and coverage criteria in AMPS cellular systems state that 75% of users rate the voice quality between good and excellent in 90% of the served area, which is usually flat terrain.
Coverage criteria and voice quality would be managed as per several terrain conditions.
For hilly terrain, 90% of the users should rate voice quality as good or excellent in 75% of the served area. For a low-cost system and a low-performance, a system operator can lower the percentage values stated above.
(b) Required Grade of Service - At the time of the busy hour, the grade of service for a normal start-up system is specified for a blocking probability of 0.02 for initiating calls. But, the blocking probability at every cell site will be different. A good system plan and a sufficient number of radio channels are needed to reduce the blocking probability.
(c) Number of Dropped Calls - When one call is dropped and P-1 calls are completed during P calls in an hour, then the call drop rate is 1/P. This call drop rate should be kept low. A high call drop rate could occur due to either handoff problems or coverage problems related to not enough availability of the channel.
(iii) Special Features - A system would like to give as many special features as possible, like a voice stored (VSR) box, automatic roaming, call forwarding, call waiting, or navigation services.
But, for these types of special services sometimes the users may not be willing to pay extra charges.
Conclusion -
our exploration of the basic cellular system has unveiled the intricate web of components and principles that govern mobile communication. From the fundamental units comprising cell sites, mobile units, and mobile telephone switching offices to the mechanisms enhancing capacity in cellular systems, each element plays a crucial role in shaping the efficiency and effectiveness of modern communication networks.
The adoption of hexagonal cells, inspired by the cellular concept, reflects a strategic choice to optimize transmission efficiency and minimize gaps in coverage.
This deliberate design not only enhances the overall performance of cellular systems but also contributes to the seamless connectivity we experience in our daily lives. I hope you all find this blog useful.
Thank you.
Do you dream of turning your thoughts and words into income ? join us now and become blogger now.



0 Comments
Leave a Comment